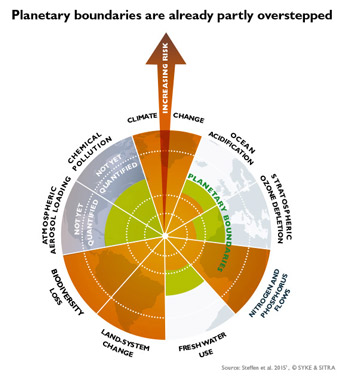
Picture. The planetary boundaries (green line) have already been overstepped in climate change, biodiversity loss, flows of nitrogen and phosphorus, and land use change. Planetary boundary processes are interlinked. Source: Steffen et al. 2015. © SYKE & SITRA. The picture is link to the larger file.
Science on climate change and other global environmental risks is becoming more and more detailed and robust. Risks that target important global environmental processes have been evaluated in studies examining planetary boundaries (Rockström et. al. 2009; Steffen et.al. 2015). Based on the precautionary principle, these studies define boundaries for nine global processes that have already been seriously altered by human activity.
The planetary boundaries for climate change and biodiversity loss are the most critical for global sustainability. Other planetary boundary processes also affecting global sustainability are ocean acidification, change in biogeochemical flows, such as altered nitrogen and phosphorus cycles, land use change, fresh water use, chemical pollution and ozone depletion, atmospheric aerosol loading, and the release of new compounds, such as plastics, into the environment.
There are a total of nine critical boundaries, and at least four of them have already been exceeded. The boundaries which have been exceeded include climate change, loss of biodiversity, land utilised by people, and biogeochemical pollution.
Will the earth remain habitable?
As a result of transgressing planetary boundaries, human activity is currently disturbing the earth's climate and its ecosystems and is causing risks for the world economy, for instance. If climate change and species loss gets out of control, conditions on the earth will become disadvantageous for human communities. Ultimately it is a question of whether or not the planet will remain habitable for people.
Researchers warn that conditions on the earth can undergo irreversible change. The latest research (Steffen et. al. 2018) stipulates on the basis of feedback processes that just two degrees of warming is a critical boundary. But already an increase of just 1 - 2 degrees can cause extensive changes on the earth which can further accelerate climate change.
The risks are great especially if the increase in temperature moves forward fast in just a century or two. Risks will affect health, the economy, and political stability. Food security will weaken and inequality between rich and poor will increase.
A global mass extinction of species is also under way. Causes include population growth and the growth of production and consumption. According to the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), biodiversity loss caused by human activity already threatens the well-being of 3.2 billion people.